Karma is a natural law. Karma is the currency of your life. With the currency of karmic actions, you purchase and create all your life experiences — good, bad, pleasant, and unpleasant. Karma is the law of cause and effect by which each individual creates his own destiny by his thoughts, words, and deeds.
According to the theory of karma, you have a cupboard filled with karmas: personal karmas, cultural karmas, and karmas that involve the entire human race. The life you experience is a mesh of all your karmas interacting with one another like a big, unique, karmic thumbprint.
Basically, if you push something, it moves. Now expand this idea and realize that the entire universe is made up of movements and reactions to movements.
Your body was created by the lovemaking movements of your parents and then movements of the sperm burrowing into the egg, zygotes replicating, organs forming, and nutrients being assimilated. Everything that keeps your body alive right now is made up of movements: visible movements, invisible movements, and millions of teeny-tiny electro-chemical movements.
The entire universe consists of spinnings upon spinnings — from galaxies to communities, to electrons circling the nucleus of an atom. Movement is the nature and quality of all creation. So what’s keeping it all going?
You can think of the universe as running on the fuel of karma. As Newton’s law of action says, every action has an equal and opposite reaction. Thus work the ways of karma.
Each individual creates their own karma by experiencing results, their ability to learn, and their disregard for experiencing. We creates our own capacities and limitations. Karma is the need to know more about a feeling, or an action, to make one’s knowledge more complete and whole. It is the necessity to experience an action or thought more fully, or from a different perspective, so that you understand it as completely as possible in order to maintain balance in your mental creations. You cannot project perfect creations unless you understand the materials, tools, and processes of creation completely, and have experienced the repercussions of your actions.
A person exists to experience all forms of materiality, to understand each thoroughly, and to learn how to manipulate and maintain these forms in balance and harmony. As the individual evolves, studies his progress and finds there is a gap in his understanding, at some point in time the gap must be filled with the appropriate experience to balance it out. Karma is, therefore, the need to experience, and to fill gaps in the understanding of the experiences gained. It is a lack of understanding of all the points of view that apply, that must be changed, and an awareness that is necessary to be gained.
Karma
The law of Karma (Sanskrit), or Kamma (Pali) originated in the Vedic system of religion, otherwise known as Hinduism. As a term, it can at the latest be traced back to the early Upanishads, around 1500 BCE.
In its major conception, karma is the physical, mental and supramental system of neutral rebound, “cause and effect,” that is inherent in existence within the bounds of time, space, and causation. Essentially what this means is that the very being which one experiences (say, as a human being) is governed by an immutable preservation of energy, vibration, and action. It is comparable to the Golden Rule but denies the ostenisble arbitrariness of Fate, Destiny, Kismet, or other such Western conceptions by attributing absolute reason and determinism to the workings of the cosmos.
Karma, for these reasons, naturally implies reincarnation since thoughts and deeds in past lives will affect one’s current situation. Thus, humanity (through a sort of collective karma) and individuals alike are responsible for the tragedies and good ‘fortunes’ which they experience. The concept of an inscrutable “God” figure is not necessary with the idea of karma. It is vital to note that karma is not an instrument of a god, or a single God, but is rather the physical and spiritual ‘physics’ of being. As gravity governs the motions of heavenly bodies and objects on the surface of the earth, karma governs the motions and happenings of life, both inanimate and animate, unconscious and conscious, in the cosmic realm.
Thus, what certain philosophical viewpoints may term “destiny” or “fate” is in actuality, according to the laws of karma, the simple and neutral working out of karma. Many have likened karma to a moral banking system, a credit and debit of good and bad. However, this view falls short of the idea that any sort of action (action being a root meaning of ‘karma’), whether we term it ‘good’ or ‘bad’, binds us in recurring cause and effect. In order to attain supreme consciousness, to escape the cycle of life, death, and rebirth and the knot of karma one must altogether transcend karma. This method of transcendence is variously dealt with in many streams of not only Hinduism and Buddhism, but other faiths and philosophical systems as well.
From Hinduism the concept of karma was absorbed and developed in different manners in other movements within the other Indian subcontinental (South Asian) religions of Buddhism, Jainism, and Sikhism. Although these religions express significant disagreement regarding the particularities of “karma”, all four groups have relatively similar notions of what karma is.
More recently the concept has been adopted (with various degrees of accuracy and understanding) by many New Age movements, Theosophy and Kardecist Spiritualism.
All living beings are alike and yet amongst all the living beings that we can normally perceive, there are many differences. For instance, some of us are wealthy, some are less wealthy, some are strong and healthy, others are disabled and so forth. There are many differences amongst living beings and even more so there are differences between animals and human beings. These differences are due to karma.
What we all share – desire, ill-will and ignorance – are common to all living beings, but the particular condition in which we find ourselves is the result of our particular karma that conditions the situation in which we find ourselves, the situation in which we may be wealthy, strong and so forth. These circumstances are decided by karma. It is in this sense that karma explains the differences amongst living beings. It explains why some beings are fortunate while others are less fortunate, some are happy while others are less happy. Karma explains the differences between living beings. You might also recall that the understanding of how karma affects the birth of living beings in happy or unhappy circumstances — the knowledge of how living beings move from happy circumstances to unhappy circumstances, and vice versa, from unhappy to happy circumstances as a result of their karma. It is karma that explains the circumstances that living beings find themselves in.
Karma is not fate or predestination. If karma is not fate or predestination, then what is it? Let us look at the term itself. Karma means action, means “to do”. Immediately we have an indication that the real meaning of karma is not fate because karma is action. It is dynamic. But it is more than simply action because it is not mechanical action. It is not unconscious or involuntary action. It is intentional, conscious, deliberate, willful action. How is it that this intentional, will action conditions or determines our situation? It is because every action must have a reaction, an effect. This truth has been expressed in regard to the physical universe by the great physicist Newton who formulated the law which states that every action must have an equal and opposite reaction. In the moral sphere of conscious actions, we have a counterpart to the physical law of action and reaction, the law that every intentional, will action must have its effect. This is why we sometimes speak either of Karma-Vipaka, intentional action and its ripened effect, or we speak of Karma-Phala, intentional action and its fruit. It is when we speak of intentional action together with its effect or fruit that we speak of the Law of Karma.
In its most basic sense, the Law of Karma in the moral sphere teaches that similar actions will lead to similar results. Let us take an example. If we plant a mango seed, the plant that springs up will be a mango tree, and eventually it will bear a mango fruit. Alternatively, if we plant a Pong Pong seed, the tree that will spring up will be a Pong Pong tree and the fruit a Pong Pong. As one sows, so shall one reap. According to one’s action, so shall be the fruit. Similarly, in the Law of Karma, if we do a wholesome action, eventually we will get a wholesome fruit, and if we do an unwholesome action eventually we will get an unwholesome, painful result. This is what we mean when we say that causes bring about effects that are similar to the causes. This we will see very clearly when we come to specific examples of wholesome and unwholesome actions.
We can understand by means of this general introduction that karma can be of two varieties – wholesome karma or good karma and unwholesome karma or bad karma. In order that we should not misunderstand this description of karma, it is useful for us to look at the original term. In this case, it is kushala or akushala karma, karma that is wholesome or unwholesome. In order that we understand how these terms are being used, it is important that we know the real meaning of kushala and akushala. Kushala means intelligent or skilful, whereas akushala means not intelligent, not skilful. This helps us to understand how these terms are being used, not in terms of good and evil but in terms of skilful and unskilful, in terms of intelligent and unintelligent, in terms of wholesome and unwholesome. Now how wholesome and how unwholesome? Wholesome in the sense that those actions which are beneficial to oneself and others, those actions that spring not out of desire, ill-will and ignorance, but out of renunciation, loving-kindness and compassion, and wisdom.
One may ask how does one know whether an action that is wholesome or unwholesome will produce happiness or unhappiness. The answer is time will tell. As long as an unwholesome action does not bear its fruit of suffering, for so long a foolish person will consider that action good. But when that unwholesome action bears its fruit of suffering then he will realize that the action is unwholesome. Similarly, so long as a wholesome action does not bear its fruit of happiness, a good person may consider that action unwholesome. When it bears its fruit of happiness, then he will realize that the action is good. So one needs to judge wholesome and unwholesome action from the point of view of long-term effect. Very simply, wholesome actions result in eventual happiness for oneself and others, while unwholesome actions have the opposite result, they result in suffering for oneself and others.
The fruit of these unwholesome actions can take various forms. The fully ripened fruit of the unwholesome actions consists of rebirth in the lower realms, in the realms of suffering — hell, hungry ghosts and animals. If these unwholesome actions are not sufficient to result in rebirth in these lower realms, they will result in unhappiness in this life as a human being. Here we can see at work the principle of a cause resulting in a similar effect. While unwholesome actions produce unwholesome results – suffering, wholesome actions produce wholesome results – happiness.
Karma, be it wholesome or unwholesome, is modified by the conditions under which the actions are performed. In other words, a wholesome or unwholesome action may be more or less strong depending upon the conditions under which it is done. The conditions which determine the weight or strength of karma may be divided into those which refer to the subject — the doer of the action — and those which refer to the object — the being to whom the action is done. So the conditions that determine the weight of karma apply to the subject and object of the action.
There are five conditions that modify the weight of karma and they are persistent, repeated action; action done with great intention and determination; action done without regret; action done towards those who possess extraordinary qualities; and action done towards those who have benefited one in the past. Here too there are subjective and objective conditions. The subjective conditions are persistent action; action done with intention; and action done without regret. If one does an unwholesome action again and again with great intention and without regret, the weight of the action will be enhanced. The objective conditions are the quality of the object to whom actions are done and the nature of the relationship. In other words, if one does a wholesome or unwholesome action towards living beings who possess extraordinary qualities such as the arhats, or the Krishna, the wholesome or unwholesome action done will have greater weight. Finally the power of wholesome or unwholesome action done towards those who have benefited one in the past, such as one’s parents, teachers and friends, will be greater.
The objective and subjective conditions together determine the weight of karma. This is important because understanding this will help us to understand that karma is not simply a matter of black and white, or good and bad. Karma is moral action and moral responsibility. But the working of the Law of Karma is very finely tuned and balanced so as to match effect with cause, so as to take into account the subjective and objective conditions that determine the nature of an action. This ensures that the effects of actions are equal to and similar to the nature of the causes.
The effects of karma may be evident either in the short term or in the long term. Traditionally we divide karma into three varieties related to the amount of time that is required for the effects of these actions to manifest themselves. Karma can either manifest its effects in this very life or in the next life or only after several lives. When karma manifests its effects in this life, we can see the fruit of karma within a relatively short length of time. This variety of karma is easily verifiable by any of us. For instance, when someone refuses to study, when someone indulges in harmful distractions like alcohol and drugs, when someone begins to steal to support his harmful habits; the effects will be evident within a short time. They will be evident in loss of livelihood and friendship, health and so forth. We cannot see the long-term effect of karma, but the Buddha and His prominent disciples who have developed their minds are able to perceive directly the long-term effects.
Besides the two varieties of karma, wholesome and unwholesome karma, we should mention neutral or ineffective karma. Neutral karma is karma that has no moral consequence either because the very nature of the action is such as to have no moral consequence or because it is done involuntarily and unintentionally. For example, sleeping, walking, breathing, eating, handicraft and so forth in themselves have no moral consequence. Similarly, unintentional action is ineffective karma. In other words, if one accidentally steps on an insect, being unconscious of its existence, this also constitutes neutral karma because there is no intention – the intentional element is not there.
The benefits of understanding the Law of Karma are that this understanding discourages one from performing unwholesome actions which have suffering as their fruit. Once we understand that in our own life every action will have a similar and equal reaction, once we understand that we will experience the effect of that action, wholesome or unwholesome, we will refrain from unwholesome behavior, not wanting to experience the effects of these unwholesome actions. And similarly, understanding that wholesome actions have happiness as their fruit, we will cultivate these wholesome actions. Reflecting on the Law of Karma, of action and reaction in the moral sphere encourages us to renounce unwholesome actions and cultivate wholesome actions.



 The Definition – What is holistic healing?
The Definition – What is holistic healing?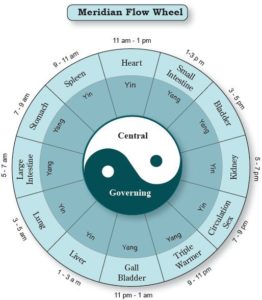 Meridians of the body are undetectable to the naked eye yet we couldn’t live without them. They influence every organ and physiological system in the body. Meridians carry energy throughout the body; similar to the way the arteries carry blood. This energy is often referred to as chi, qi or prana.
Meridians of the body are undetectable to the naked eye yet we couldn’t live without them. They influence every organ and physiological system in the body. Meridians carry energy throughout the body; similar to the way the arteries carry blood. This energy is often referred to as chi, qi or prana.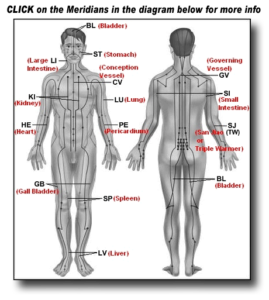 These meridians of the body are in control of not only their corresponding organ, but also additional organs around them. They play a specific and crucial role in the health of the entire system. Energetic imbalances on either side, whether meridians are energy deficient or energy excessive causes problems for the organ systems they regulate. Balance is key in the body and the energy in the meridians is no different.
These meridians of the body are in control of not only their corresponding organ, but also additional organs around them. They play a specific and crucial role in the health of the entire system. Energetic imbalances on either side, whether meridians are energy deficient or energy excessive causes problems for the organ systems they regulate. Balance is key in the body and the energy in the meridians is no different. Sometimes we face incessant problems and despite best efforts there is no respite. So much so that the entire family has a dark could over it where all members are suffering. This suffering cloud include problems such as marital disharmony, addictions, miscarriages, feuds within family members and financial problems. We are bewildered and try to overcome them but we are kept at bay because the root of such problems lies in the spiritual dimension. These problems are caused by our deceased ancestors. Such ancestral problems are levied to us descendants so that we take notice and help them in their afterlife. One of the reasons why all family members are affected is because they have the same ancestors. It is a cry of hope by our deceased ancestors as after death they are in the form of a subtle body or spirits and cannot do spiritual practice. Very simple and basic daily efforts can help alleviate our ancestral distress and give momentum to ancestral spirits in their afterlife.
Sometimes we face incessant problems and despite best efforts there is no respite. So much so that the entire family has a dark could over it where all members are suffering. This suffering cloud include problems such as marital disharmony, addictions, miscarriages, feuds within family members and financial problems. We are bewildered and try to overcome them but we are kept at bay because the root of such problems lies in the spiritual dimension. These problems are caused by our deceased ancestors. Such ancestral problems are levied to us descendants so that we take notice and help them in their afterlife. One of the reasons why all family members are affected is because they have the same ancestors. It is a cry of hope by our deceased ancestors as after death they are in the form of a subtle body or spirits and cannot do spiritual practice. Very simple and basic daily efforts can help alleviate our ancestral distress and give momentum to ancestral spirits in their afterlife.